GDOES HORIBA Presents in the Aluminum Packaging Industry
2022-12-21
How can I determine the thickness of the varnish layer?
Which product/packaging compatibility studies correspond to the food packaging company?
Aluminum can be considered as the most versatile packaging material in the world, with the ability to shape any shape, its protective qualities and its ability to be completely recycled and reused an infinite number of times, the use of aluminum in the packaging industry has become increasingly interesting. Despite having a higher cost of production than a glass bottle, aluminum cans are lighter and do not break, which makes the use of this material in production significantly cheaper.

Even when reduced to thin sheets, the strength and unique physical properties of aluminum offer excellent protection against the effects of oxygen, light, moisture, microorganisms and unwanted odors. However, for each application, specific surface finishing treatments have been developed, allowing for better corrosion resistance in various environments and the promotion of durable adhesive bonds with polymer films, lacquers and paints. For this reason, RF-GDOES, with its rapid erosion rate, can be considered as an efficient technique for the evaluation of problem solving during manufacturing.
Being aluminum is a light and abundant material that is easy to handle, which allows weight and energy savings when used as a container. With a thickness of a few microns it is ideal to protect all the products it contains against light, humidity, air and microorganisms, for this reason aluminum has become an ideal material to use it for the manufacture of packaging, maintaining the essential qualities in food, its organoleptic properties (hygiene, aromas, tastes, smells, perfumes and colors), as one of the main applications.
GD Profiler 2 couples an advanced pulsed RF-GD source to a high-resolution, wide-spectral-range optical emission spectrometer. The precise and fast cathodic spraying of a representative area of the investigated sample (usually a crater of 4 mm diameter) is ensured by means of a source of RF pulses, which also allows the reduction of the thermal load on the sample, and a deeper resolution, which is fundamental for the identification of surface treatments. All the elements of interest are measured simultaneously, depending on the sputtering time, using a spectrometer.
The RF-GD-OES can be used to discriminate between good and bad batches, that is, with regard to the last step of the process, when the lacquer is applied and the adhesion problems are solved. RF-GDOES can highlight the difference between the batches. Such Al samples are relatively thin and therefore for correct analysis with RF-GDOES it is necessary to cut and glue them on a rigid substrate using a copper tape, as shown:
Thanks to the pulsed mode, the phosphating and chromatizing layers on the surface of aluminum sheets can be solved efficiently. All useful information can be obtained in the first 30 seconds of the analysis, which makes this technique extremely interesting for such industries.

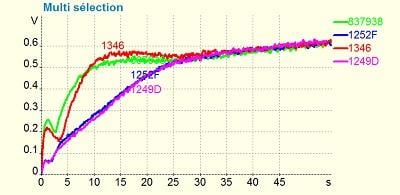
According to the packaging manufacturer, when performing adhesion tests for lacquer application, a “good” batch (samples 1249 D and 1252F) and a “bad” batch (samples 837938 and 1346) can be identified. When studying the conversion coatings, no particular differences between the different samples can be highlighted. The peaks of P and Cr do not show a specific trend that can be associated with the classification of “good” or “bad” lots, however, differences between suppliers can be identified.


The GDSOES analysis method can be used to efficiently and quickly compare batches of materials from different suppliers, which allows the rapid detection of characteristics detrimental to the manufacturing process.
Aluminum containers for each application have developed specific surface finishing treatments, which allows for better corrosion resistance in various environments and the promotion of durable adhesive bonds with polymer films, lacquers and paints. For this reason, RF-GDOES, with its rapid erosion rate, can be considered as an efficient technique for the evaluation of quality control in manufacturing.
Success Story
In aluminum containers and packaging for the pharmaceutical and food industry, quality control is very important, since its primary purpose is to protect its contents to the final consumer.
One of the advantages of aluminum that makes it an ideal packaging is that it is sterile and hygienic, resistant to corrosion, protects the contents for long periods of time, they are light to cool drinks and it is difficult to break, it is non-toxic, recyclable, high resistance among others,
Aluminum and its various layers in order to avoid decomposition and help the preservation, color and flavor of products, it is important to have an instrument capable of analyzing the composition of aluminum containers in layers.
There are different thicknesses of aluminum sheets it all depends on the content to be packed, for example, in the dairy industry a thickness of 30 to 30 µm is used. in the case of chocolates it is between 7 to 15 µ, if what you want to pack are acidic or alkaline foods then composite films are used to avoid direct contact with the metal.
Therefore, the quality control of aluminum packaging is very important to comply with national and international regulations for this purpose. In such a way as to ensure the protection of consumers’ health.
Horiba has developed the analysis method to guarantee the analysis of all its layers and possible impurities during the production of containers with the GDS-OES Profiler 2 obtaining excellent results.
The success story is: According to the packaging manufacturer, when performing the adhesion tests for the lacquer application, a “good” batch (samples 1249 D and 1252F) and a “bad” batch (samples 837938 and 1346) can be identified. When studying the conversion coatings, no particular differences between the different samples can be highlighted. The peaks of P and Cr do not show a specific trend that can be associated with the classification of “good” or “bad” lots, however, differences between suppliers can be identified.